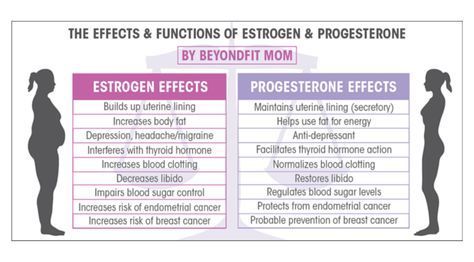
Weight management is a topic that affects millions of people worldwide. While diet and exercise play significant roles
in maintaining a healthy weight, many individuals struggle to achieve their desired goals. One crucial factor that
should not be overlooked in weight management is the role of hormones. Hormones, the chemical messengers in our bodies,
can have a profound impact on our metabolism, appetite, and overall body composition. Understanding how hormones influence
weight management can provide insights into developing more effective strategies for achieving and maintaining a healthy
weight.
Leptin: The Satiety Hormone
Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that plays a critical role in regulating appetite and body weight. It acts
as a satiety hormone, signaling to the brain that we are full and should stop eating. When leptin levels are low,
it can lead to increased hunger and overeating. On the other hand, high levels of leptin may result in reduced appetite
and a decrease in food intake. Therefore, maintaining a healthy balance of leptin is crucial for weight management.
Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone
Ghrelin is often referred to as the hunger hormone. This hormone is primarily produced in the stomach and stimulates
appetite. Ghrelin levels typically rise before meals and decrease after eating. It signals to the brain that it’s time
to eat and helps in regulating energy balance. However, for individuals struggling with weight management, ghrelin
imbalances may contribute to excessive hunger and cravings, making it more challenging to achieve weight loss goals.
Understanding the role of ghrelin can help develop strategies to manage its effects on appetite and food intake.
Insulin: The Blood Sugar Regulator
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas that plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. When we consume
carbohydrates, insulin helps transport glucose from the bloodstream into our cells to be used as energy or stored
as glycogen in the liver and muscles. It also inhibits the breakdown of stored fat. However, insulin resistance can
occur when the body’s cells do not respond to insulin properly. This can lead to higher insulin levels in the blood,
which promotes fat storage and inhibits fat burning. Managing insulin levels through lifestyle modifications, such
as following a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity, is crucial for weight management.
Cortisol: The Stress Hormone
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, is produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. While cortisol
plays a critical role in our body’s stress response, prolonged periods of stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels
that may contribute to weight gain. High cortisol levels can increase appetite, particularly for high-calorie foods,
and promote the storage of fat, particularly in the abdominal region. Therefore, managing stress levels through relaxation
techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep is vital for weight management.
Thyroid Hormones: The Metabolic Regulators
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate our body’s metabolism. These hormones, known as thyroid hormones
(T3 and T4), play a crucial role in determining how efficiently our body burns calories. Hypothyroidism, a condition
where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, can lead to a slow metabolism and weight gain. Conversely,
hyperthyroidism, a condition characterized by excessive thyroid hormone production, can result in a fast metabolism
and weight loss. Maintaining a healthy thyroid function is essential for managing weight effectively.
Conclusion
Hormones play a significant role in weight management, affecting our appetite, metabolism, and body composition. Understanding
the impact of hormones such as leptin, ghrelin, insulin, cortisol, and thyroid hormones on weight regulation is essential.
By considering hormonal factors and adopting strategies to keep them in balance – such as following a balanced diet,
managing stress levels, engaging in regular physical activity, and ensuring proper thyroid function – we can optimize
weight management efforts. It is important to remember that weight management is a complex process and requires a holistic
approach that considers various factors including hormones.